Zero Gravity Seats : NASA-Inspired Ergonomics Redefining Comfort in NEVs
As the global new energy vehicle (NEV) market surges forward, delivering superior ride comfort has become a vital strategy to stand out in a competitive landscape. One standout innovation gaining traction is the “Zero Gravity Seat”—a technology rooted in NASA’s ergonomic research. This blog explores the origin, science, benefits, and real-world application of Zero Gravity seating, helping NEV exporters attract high-end buyers through compelling tech storytelling.
Catalog
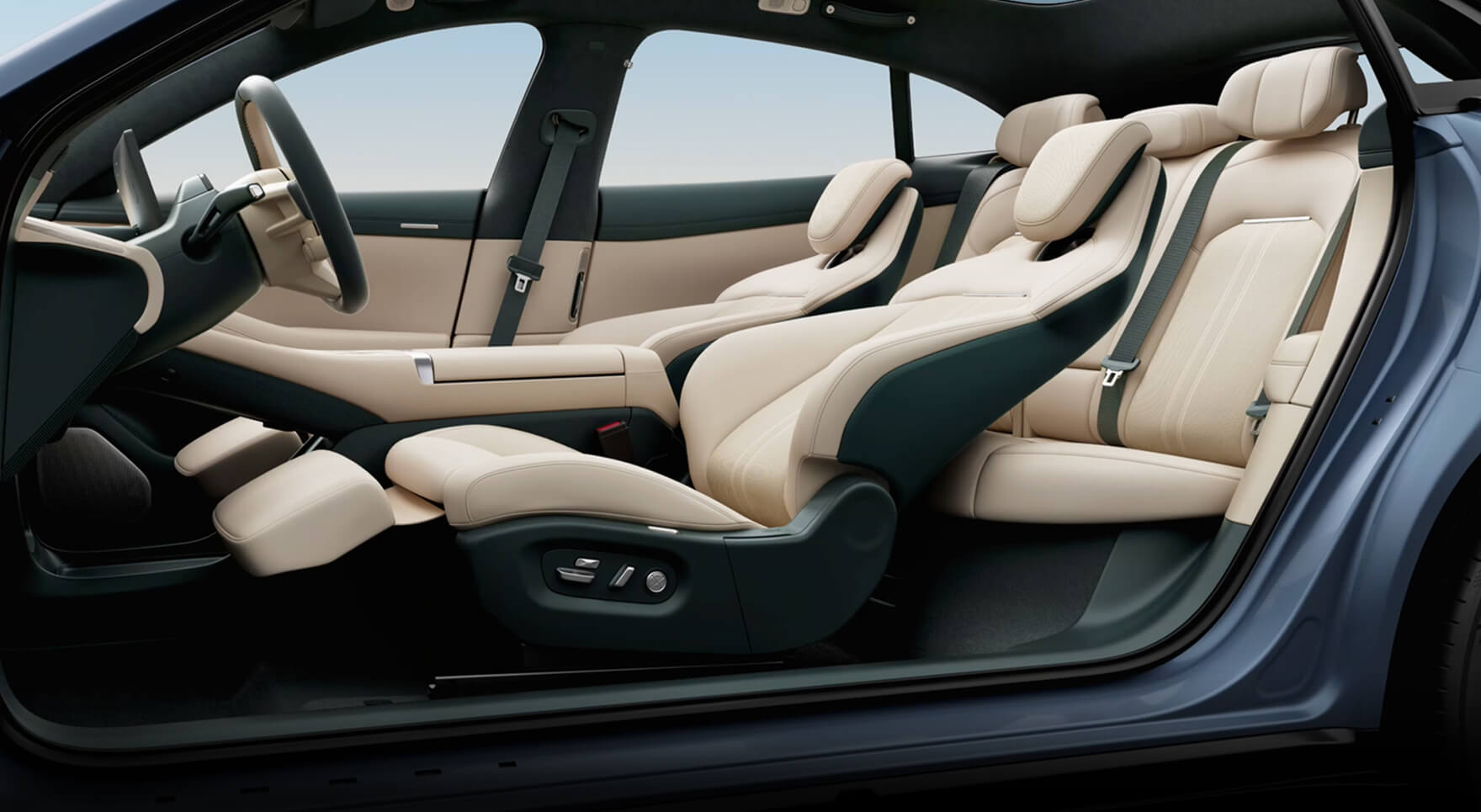

1. From Space to the Streets: The Origins of Zero Gravity Seats
The concept of the Zero Gravity Seat stems from NASA’s research during its manned space missions in the 1970s, particularly the Skylab program. NASA sought to identify the most naturally relaxed human posture in a zero-gravity environment, aiming to design optimal sleep equipment for astronauts.
The result was the Neutral Body Posture (NBP)—a relaxed position where the body naturally floats with:
An S-shaped spine
Relaxed limbs
Slightly bent knees and hips
Naturally curved neck and shoulders
This posture, measured at 128°±7°, became the blueprint for what we now call the “zero gravity” position. Recognized for its ability to reduce skeletal and muscular stress, it was later standardized in NASA’s Man-Systems Integration Standards (MSIS) and eventually adapted into automotive seat design by brands like Nissan, Infiniti, and Hyundai.
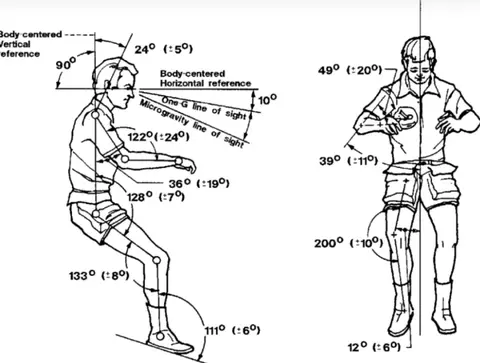
2. What Makes It “Zero Gravity”?
The NBP replicates how the human body positions itself when freed from Earth’s gravitational pull. Key ergonomic features include:
Natural S-curve spinal support: Balanced pressure distribution across the neck, thoracic, and lumbar regions.
Relaxed hip and knee angles: Reducing lower limb fatigue and numbness.
Loose shoulders and forward-bent arms: Preventing upper limb tension.
Upward-tilted toes: Encouraging blood flow in the legs.
These elements help delay fatigue, creating a floating-like experience even on long rides—hence the name “Zero Gravity.”
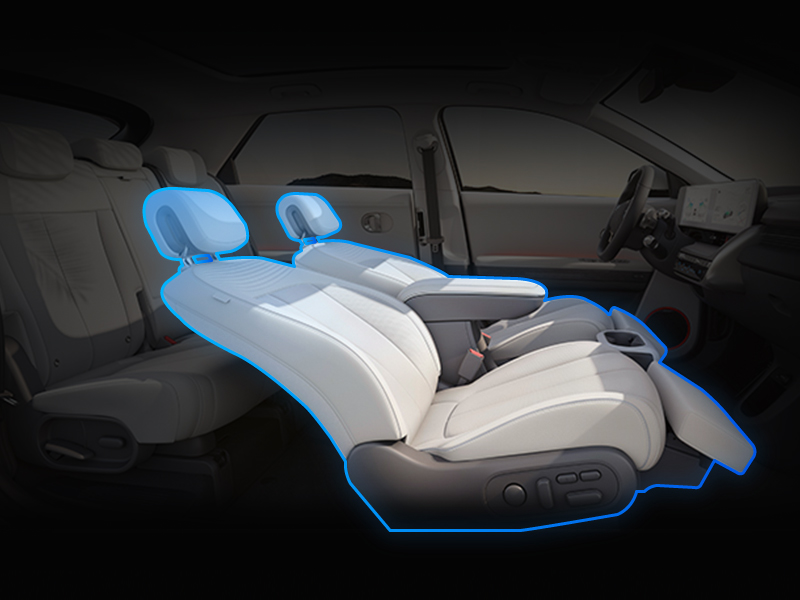

3. Ergonomics in Action: How Seats Are Engineered
✅ Pressure Mapping with Multi-Zone Support
Take Nissan’s Zero Gravity seats, for instance—they feature 14 pressure points spanning the pelvis, spine, and shoulders. Varying foam densities are used to provide firm support at load-bearing zones and softness in cushioning areas.
✅ Adaptive Backrest Structure
The seat back is split into upper and lower sections with flexible joints, allowing the seat to conform to individual body shapes. This preserves the spine’s natural curvature and minimizes muscular stress.
✅ Verified by Biometrics and Road Tests
In collaboration with Keio University’s Yamazaki Lab, Nissan conducted trials measuring driver fatigue using blood lactate levels, heart rate, and subjective fatigue scores. Results showed over 50% reduction in fatigue compared to conventional seats.
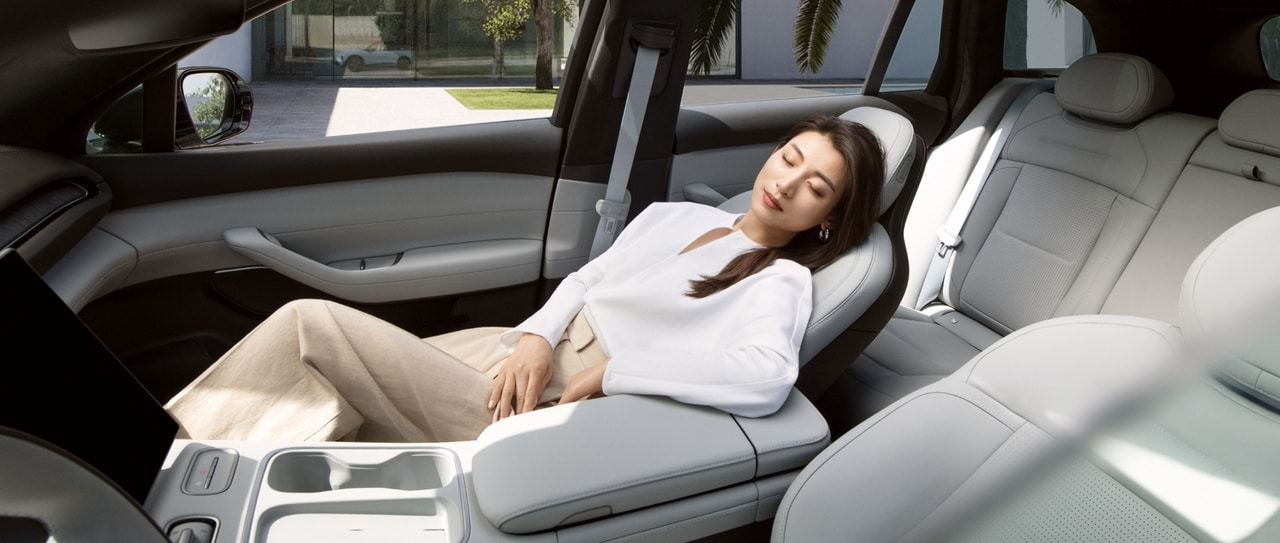

4. Real-World Benefits for Drivers and Passengers
🌟 Reduced Fatigue, Better Focus
With optimal spinal support and even pressure distribution, Zero Gravity seats prevent slouching or incorrect posture—key factors in long-haul fatigue.
💉 Improved Blood Circulation
The 14-point pressure design boosts blood flow to the hips and legs, minimizing numbness and lowering the risk of varicose veins.
🛣️ Ideal for Short and Long Trips
Whether commuting in urban traffic or cruising on highways, the seats maintain consistent comfort and support—praised by U.S. AAA consumer surveys.

5. Key Safety and Design Considerations
Despite their ergonomic advantages, Zero Gravity seats introduce some safety and integration challenges:
⚠️ Seatbelt Limitations in Rear Collisions
Standard 3-point belts may not adequately restrain passengers during rear-end crashes, increasing head/neck injury risks. 4-point belts offer better control but require vehicle-wide safety redesigns.
⚠️ Recline Angle Conflicts
To achieve NBP, the seat must recline more than usual. This can disrupt alignment with airbags, headrests, and steering wheels—raising concerns over visibility and impact safety.
⚠️ Structural Risks
While failure data is mostly from home recliners, automotive seats share similar concerns: locking mechanism failure or frame collapse can pose serious risks during emergencies.

Conclusion
As a signature feature in premium NEVs, the Zero Gravity seat transforms vehicle comfort using aerospace-grade ergonomics. Built around NASA’s Neutral Body Posture, and enhanced through pressure mapping, adaptive design, and physiological testing, this seating innovation is reshaping the way we experience driving.
For Chinese NEV manufacturers and exporters, leveraging and showcasing the benefits of Zero Gravity seating offers a compelling edge in appealing to global high-end markets.
Please explore our blog for the latest news and offers from the EV market.





